FPGA RFID
This was my final project which I worked with Hannah Field on for MIT’s 6.111 (Introductory Digital Systems Lab) course.
It is an extension of the work described in my first RFID project.
In this project, we used an FPGA to create a full RFID system with the ability to read/validate MIT ID cards and spoof stored ID numbers. Our goal was to be able to read our ID cards with one FPGA, store the ID number, and transmit that to a second FPGA system running our reader. In addition, we aimed to create a portable version of this system that could be held up to an MIT ID card reader to gain access to the doorway.
For more details, see the final report.
Source code is available on Github.
Hardware Link to heading
This project was developed on Digilent’s Nexys4 DDR board, a development board for the Artix-7 FPGA. For our portable system, we switched to the Cmod A7, another development board for the Artix-7 by Digilent that has a more breadboard friendly format.
Images Link to heading
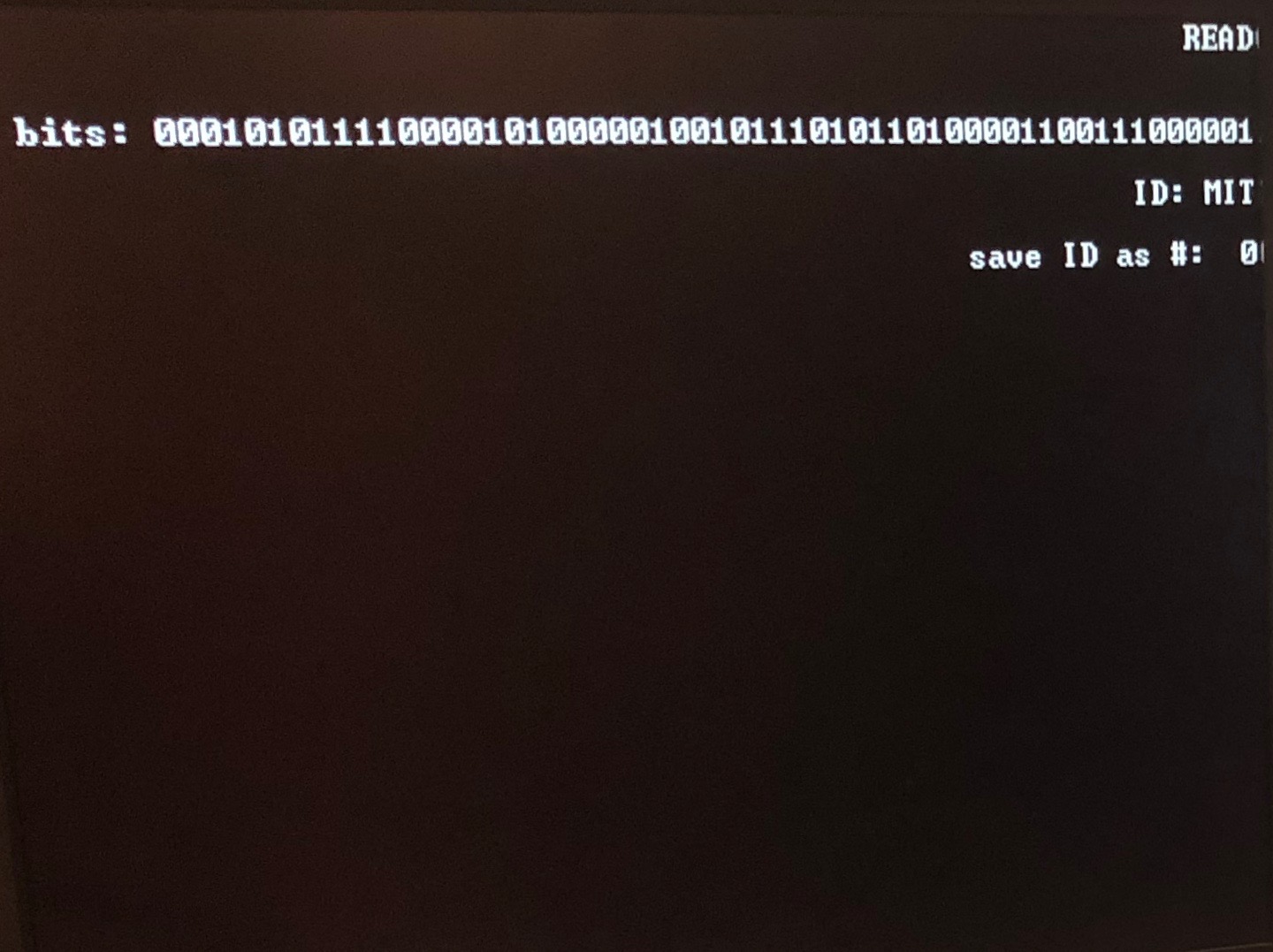
User interface during ID card reading mode. The screen displays the last valid ID number and also shows if the card is recognized as an MIT ID.

User interface during ID card spoof mode. The screen shows all 16 stored ID numbers. The buttons on the development board are used to select an ID number to spoof.
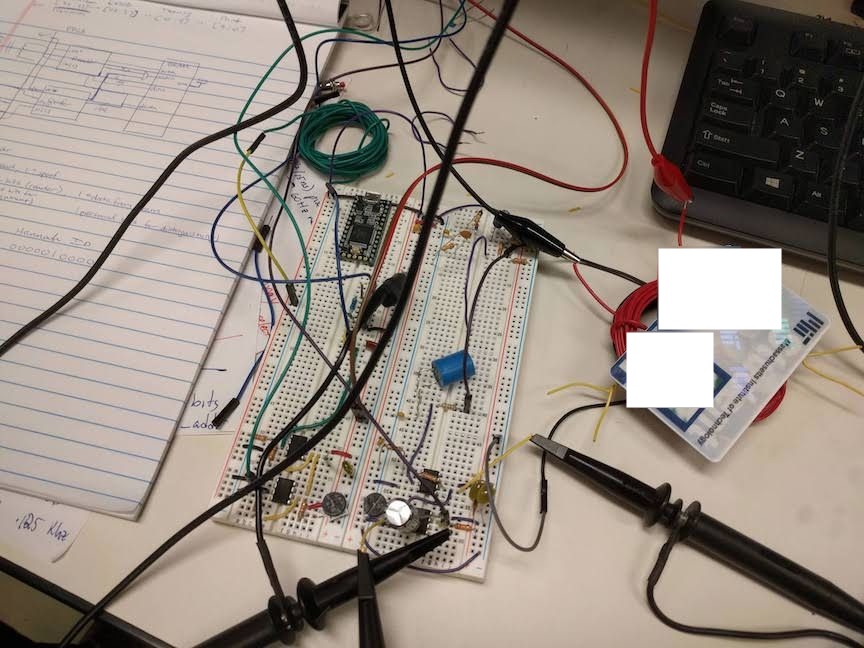
Card reader setup. The red coil is connected to a signal generator and transmits a 125 kHz sine wave. The green coil is the receive coil and is placed on top of the ID card to read the signal. The breadboard on the right contains the entirety of the card reading circuitry.